
|
|
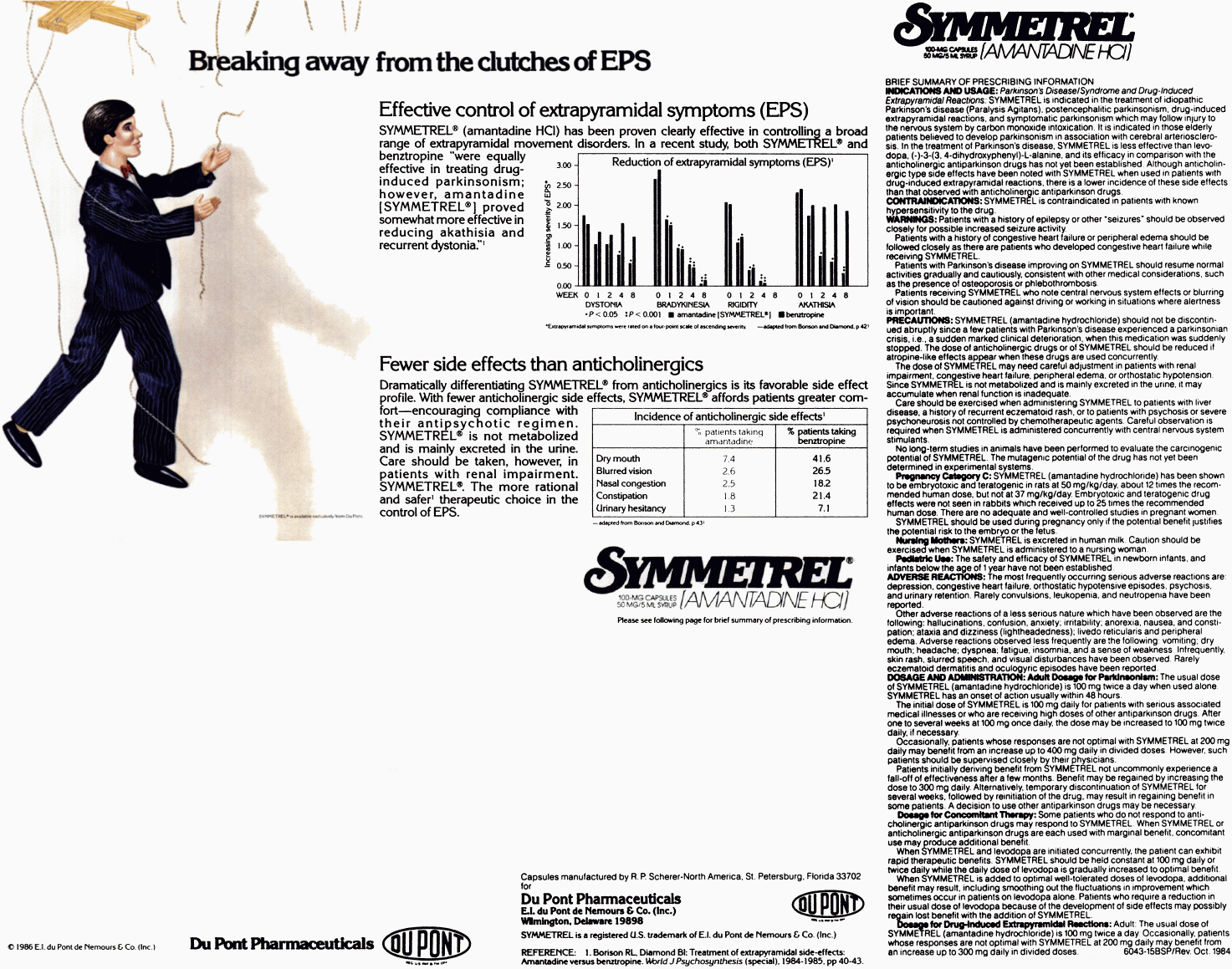
Symmetrel advertisement, 1986. American Journal of Psychiatry, Vol. 143, No. 11. Breaking away from the clutches of EPS ~ Effective control of extrapyramidal symptoms (EPS) SYMMETREL® (amantadine HCl) has been proven clearly effective in controlling a broad range of extrapyramidal movement disorders. In a recent study, both Symmetrel® and benztropine "were equally effective in treating drug-induced parkinsonism; however, amantadine (Symmetrel®) proved somewhat more effective in reducing akathisia and recurrent dystonia."(1) Reduction of extrapyramidal symptoms (EPS): DYSTONIA ~ BRADYKINESIA ~ RIGIDITY ~ AKATHISIA Extrapyramidal symptoms were rated on a four-point scale of ascending severity. Fewer side effects than anticholinergics ~ Dramatically differentiating Symmetrel® from anticholinergics is its favorable side effect profile. With fewer anticholinergic side effects, Symmetrel® affords patients greater comfort -- encouraging compliance with their antipsychotic regimen. Symmetrel® is not metabolized and is mainly excreted in the urine. Care should be taken, however, in patients with renal impairment. Symmetrel. The more rational and safer(1) therapeutic choice in the control of EPS. Incidence of anticholinergic side effects: Dry mouth ~ Blurred vision ~ Nasal congestion ~ Constipation ~ Urinary hesitancy BRIEF SUMMARY OF PRESCRIBING INFORMATION INDICATIONS AND USAGE: Parkinson's Disease/Syndrome and Drug-Induced Extrapyramidal Reactions: Symmetrel is indicated in the treatment of idiopathic Parkinson's disease (Paralysis Agitans), postencephalitic parkinsonism, drug-induced extrapyramidal reactions, and symptomatic parkinsonism which may follow injury to the nervous system by carbon monoxide intoxication. It is indicated in those elderly patients believed to develop parkinsonism in association with cerebral arteriosclerosis. In the treatment of Parkinson's disease, Symmetrel is less effective than levodopa,(-)-3-(3, 4-dihydroxyphenyl)-L-alanine, and its efficacy in comparison with the anticholinergic antiparkinson drugs has not yet been established. Although anticholinergic type side effects have been noted with Symmetrel when used in patients with drug-induced extrapyramidal reactions, there is a lower incidence of these side effects than that observed with anticholinergic antiparkinson drugs. ADVERSE REACTIONS: The most frequently occurring serious adverse reactions are: depression, congestive heart failure, orthostatic hypotensive episodes, psychosis, and urinary retention. Rarely convulsions, leukopenia, and neutropenia have been reported. Other adverse reactions of a less serious nature which have been observed are the following: hallucinations, confusion, anxiety; irritability; anorexia, nausea, and constipation; ataxia and dizziness (lightheadedness); livedo reticularis and peripheral edema. Adverse reactions observed less frequently are the following: vomiting; dry mouth; headache; dyspnea; fatigue, insomnia, and a sense of weakness. Infrequently, skin rash, slurred speech, and visual disturbances have been observed. Rarely eczematoid dermatitis and oculogyric episodes have been reported. REFERENCE: 1. Borison RL, Diamond BI: Treatment of extrapyramidal side-effects: Amantadine versus benztropine. World J Psychosynthesis (special). 1984-1985, pp 40-43. © 1986 E.I. du Pont de Nemours & Co. (Inc.) Du Pont Pharmaceuticals |